William M. Arkin
Phase Zero: June 1, 2015
If you have a telephone number that has ever been called by an inmate in a federal prison, registered a change of address with the Postal Service, rented a car from Avis, used a corporate or Sears credit card, applied for nonprofit status with the IRS, or obtained non-driver’s legal identification from a private company, they have you on file.
They are not who you think they are. They are not the NSA or the CIA. They are the National Security Analysis Center (NSAC), an obscure element of the Justice Department that has grown from its creation in 2008 into a sprawling 400-person, $150 million-a-year multi-agency organization employing almost 300 analysts, the majority of whom are corporate contractors.
The Center has its roots in the Foreign Terrorist Tracking Task Force (FTTTF), a small cell established in October 2001 to look for additional 9/11-like terrorists who might have entered the United States. But with the emergence of significant “homegrown” threats in the late aughts, the Task Force’s focus was thought to be too narrow. NSAC was created to focus scrutiny on new threat, specifically on Americans, particularly Muslims, who might pose a hidden threat (the Task Force became a unit within NSAC’s bureaucratic umbrella). As Americans began traveling abroad to join al-Shabaab and then ISIS, the Center’s dragnet expanded to catch the vast pool of “youth” who also might fit a profile of either radicalism or law-breaking. Its mission runs the full gamut of “national security threats…to the United States and its interests,” according to a partially declassified Justice Department Inspector General report. That includes everything from terrorism to counter-narcotics, nuclear proliferation, and espionage.
NSAC not only has a focus beyond foreign investigations or terrorists, but in the past year-and-a-half, according to documents obtained by Phase Zero and extensive interviews with contractors and government officials who have worked with the Center and the Task Force, it has also aggressively built up a partnership with the military, taking on deep background investigations of foreign-born and foreign-connected soldiers, civilians, and contractors working for the government. Its investigations go far beyond traditional security “vetting”; NSAC scours certain select government employees, contractors and their affiliates, examining multiple layers of connected relatives and associates. And the Center hosts dozens of additional “liaison” officers from other government agencies, providing those agencies with frictionless access to private information about U.S. residents that they would otherwise not have.
Today, through a series of high-level classified authorities and commercial relationships, the Center has access to over 130 databases and datasets of information comprising some two billion records, over half of which are unique and not contained in any other government information warehouse. The Center is, in fact, according to interviews with government officials, the sole organization in the U.S. government with the authority to delve deeply into the activities and associations of foreigners and Americans alike. From its unmarked office in the Crystal City neighborhood of Arlington, Virginia, the Center can not only gain access to the full gamut of intelligence databases of the U.S. government, but also query and retain information contained in law enforcement and commercial data. It also conducts live searches, and retains classified and open datasets of identity and transactional data for later examination. In some ways then, the data that the Center accesses and regularly trawls against its data mining protocols is the FBI’s equivalent of NSA’s bulk collection, the examination of databases with the hope of finding triggers or links to terrorists rather than the specific accessing of information to look at an individual or even group of individuals.
The Center’s powerful perch—and its virtually unlimited reach—brings the federal government closer than ever to the Holy Grail of connecting every dot, a dream that has been pursued by terrorist hunters since the failures that permitted the 9/11 attacks 14 years ago. The data access and analytic methods it uses grew out of a retrospective analysis of the vast reams of data about the 19 hijackers that law enforcement and intelligence agencies had indicators off, but never acted on. The Foreign Terrorist Tracking Task Force (originally called “F-tri-F” by insiders) meticulously reconstructed the actions of the 19 hijackers and other known law-breakers—how they lived their day-to-day lives and what they did to avoid intelligence detection—to find patterns and triggers of potential wrongdoing. They created thousands of pages of chronologies covering the 19 hijackers from the moment they entered the United States, trying to recreate what each did every day they were here.
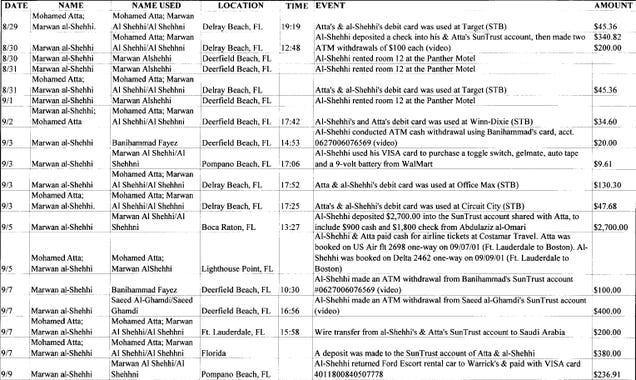
Those patterns then became profiles that could be applied to vast amounts of disparate and unstructured data to sniff out similar attributes. Those attributes, once applied to individuals, became the legal predicate for collection and retention of data. If someone fit the profile, they were worthy of a second look. They were worthy of a second look if they might fit the profile.
Beyond public records and what appears on the internet, beyond news articles or what’s in law enforcement databases—but in addition to all of those things—the mere presence of a name becomes justification enough. NSAC’s methods turn the notion of legal predicate—a logical proposition or an earlier offense that justifies law enforcement action—on its head. Using big data analysis to discover non-obvious and even clandestine links, the Center looks not just for suspects, but for what the counter-terrorism world calls “clean skins”—people with no known affiliation to terrorism or crime, needles in a giant haystack that don’t necessarily look like needles. Or people who aren’t needles at all, but who might become needles in the future and thus warrant observation today.
The American people have repeatedly rejected the notion of a domestic intelligence agency operating within our borders. Yet NSAC has become the real-world equivalent. Along the way in its development though, the Center has rarely been discussed in the federal budget or in congressional oversight hearings available to the public. And being neither solely a part of the intelligence community (IC) nor solely a law enforcement agency (and yet both), it skirts limitations that exist in each community, allowing it to collect and examine information on people who are not otherwise accused of or suspected of any crime.
(read the full article at Phase Zero)